Our NHS users can access a range of BMJ journals. Get the latest issues of your favourite journals sent to your inbox by signing up to the eTOC.
Follow
these step-by-step instructions to find whether we subscribe to the
journal title you need.
Check our
previous blog post to learn what an eTOC is.
Set up an alert
on a journal from BMJ by following the steps below:
How to subscribe to an eTOC on a BMJ journal title
1. Link to
the BMJ platform
I'm going to set up an alert for the BMJ journal title Gut. Find the journal entry on the NHS A-Z journals list. Click the
link for the BMJ on the journal title entry on the NHS A-Z journals list.
Gut journal found on the NHS A-Z journals list
You will be
taken to the journal page on BMJ.
2. Create
your alert
To create
your journal alert, just click email alerts.
Journal page for Gut on the BMJ platform
Enter your
email address and click the continue button.
Enter the email address where you want to receive the updates
You will be
prompted to set up a password if you are not already registered. This will
allow you to manage your email alert subscriptions.
Enter your password, then confirm it
You'll see a confirmation of your alert.
You will
now receive an email containing the table of contents for the journal title
when a new issue is published.
3. Access
Full-Text
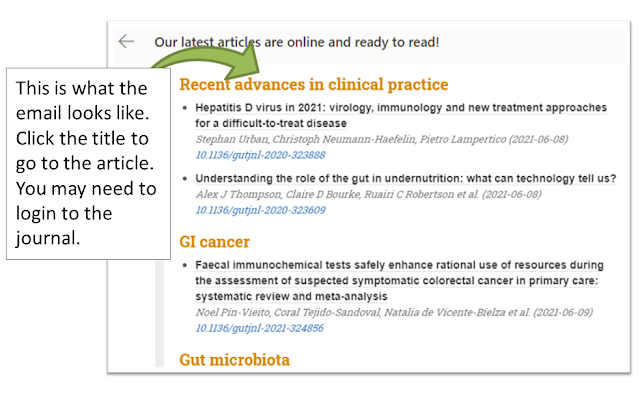
See the image below for an example of what the email will look like. Click the
article link to go to an article highlighted in the update email. You will need
to login via your OpenAthens username to access the full-text.
Example of an eToc email from BMJ for the Gut journal title
Unsubscribe
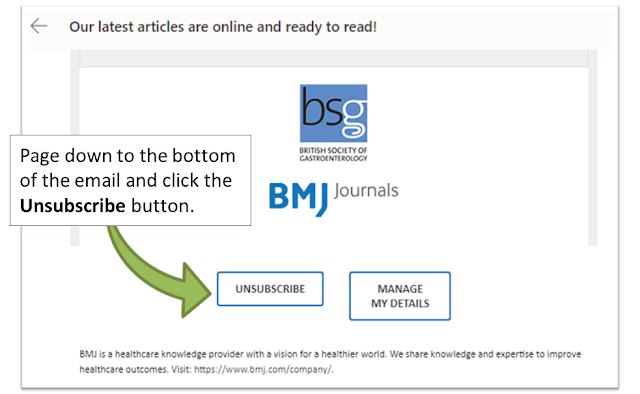
1. To stop the alerts
Page down to the bottom of the email and select the option to unsubscribe.
example of an etoc email
You will get a confirmation message that you have unsubscribed.
 |
| example of confirmation of your unsubscribe action |
More help using ejournals
- Finding NHS Journals and accessing full-text: step-by-step – instructions on how to find NHS full-text journals
- eJournals help page – for more help on how to find articles and access journals
- Contact
your eresources librarian, Cheryl, at c.kent@keele.ac.uk if you need more help.





Comments
Post a Comment